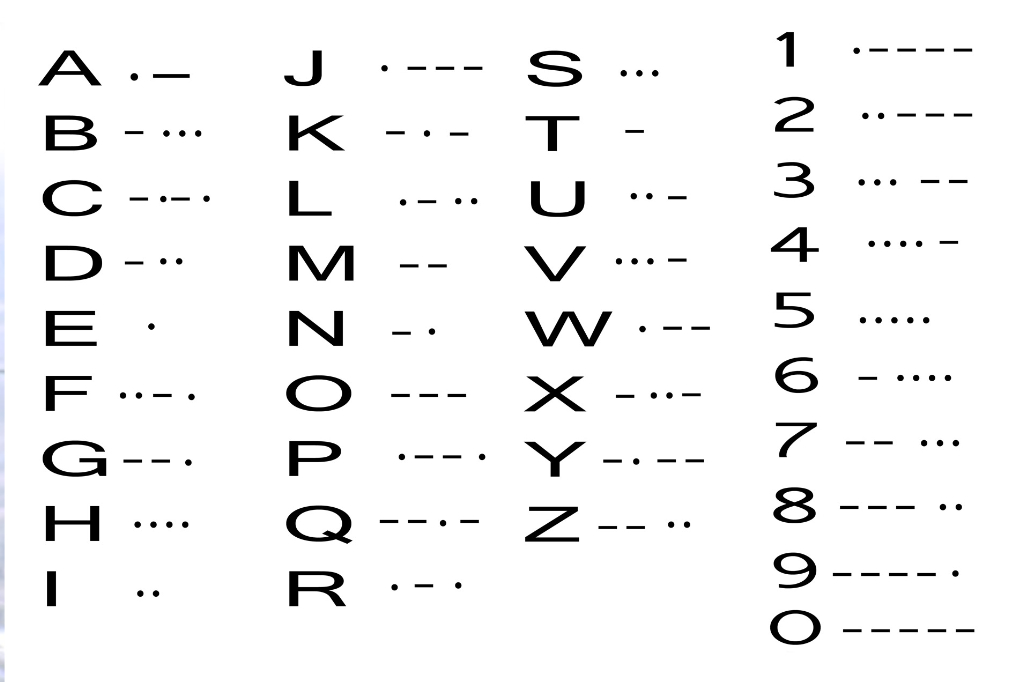
The Morse Code: From Dots and Dashes to DMs and Tweets
Not long ago, one of our team building events required a short trip to a beautiful rural area. As I was driving through the quaint mountain villages, a road sign popped into my eyes: ‘Post, telephone, telegraph’. WHAT? In the digital age? Well, this is Romania, so nothing surprises us anymore. But as the words seemed to linger in my head, I did a little bit of research and it seems it’s not only Romania. It’s Nostalgia. And it’s all over the world. Almost 200 years on and there are some people that are still using the Morse Code. And it seems that, even if the technologies differ, its principles and concepts laid a foundation that influenced the binary logic, serial communication, error detection, and encoding strategies used in digital technology.
If you want to find out more about our eCommerce projects, we are here to help.
Morse code – making history
Invented in a time when messages were delivered via horseback, no wonder that it was seen as a major breakthrough.
The two culprits, Samuel Morse and his assistant Alfred Lewis Vail. The code is made up of dots, dashes and spaces (for the connoisseurs dits and dahs). Specific combinations of these dots and dashes intertwined with spaces represent a certain letter. These signals were transmitted via electrical pulses at the beginning and then, in the 1900s, as radio signals.
Over the next decades, telegraph lines spread like wildfire and when Western Union completed the first transcontinental telegraph line in 1861, President Lincoln received its first message — sent all the way from San Francisco to Washington D.C.
We can only imagine the buzz and excitement that filled the room when the message was received from almost 3000 miles away!
What’s most interesting is the fact that the International Morse Code was used in World War II and in the Korean and Vietnam wars. It was used heavily by the shipping industry and for the safety of the seas up until the early 1990s.
Interesting fact
The internationally recognized distress signal – SOS – was first adopted in 1905 by German telegraphers. Why did they choose these specific letters? The letters are not acronyms for anything. Simply, their ‘spelling’ in Morse code – “dot-dot-dot-dash-dash-dash-dot-dot-dot” – is an easy sequence to remember, even when someone is in grave danger.
A vital element for evolution
Humans have an overwhelming need to communicate. Over time, finding easier, faster ways to communicate has been a constant preoccupation. From smoke signals and cave paintings, to present smartphones, finding better ways to communicate was the facilitator for becoming a great civilization.
The Morse code was no small feat. It had a significant impact on the way we connected, it facilitated trade and commerce and has helped to make logistics and business operations more coordinated.
Morse code marked the beginning of the communications revolution, paving the way for other inventions, such as the telephone and the internet. From there, there was no turning back. Long distances did not stand in our ways to connect, anymore.
The Morse code and the digital age
As the forerunner to email and text messages, the Morse code deserves a lot of recognition. Although the technologies are light-years apart, there is more to the Morse code than just an antique means of communication. The Morse code has influenced the development of digital communication.

While the Morse code utilises a series of dots and dashes to represent letters, numbers, and other symbols, in the binary encoding, a series of 0s and 1s is used to represent information. Both are examples of how complex information can be encoded using just two symbols.
The idea of encoding information in a simple, binary format inspired early computer scientists and engineers. They understood that complex messages could be conveyed through simple on/off signals, a principle that is central to digital computing.
The Morse code used sequential transmission of impulses over telegraph wires, a precursor to modern serial communication. Serial communication, where data is sent one bit at a time over a communication channel, remains a common method in digital data transmission today.
One other impressive feat of the Morse code is that by using rules and conventions, it laid the grounds for developing communication protocols. This led to standardised ways of transmitting and receiving information in a digital format, contributing to the development of various networking protocols.
And just as the use of spaces and timing in Morse code helped operators to detect errors, the concept of error detection and correction has evolved into more complex algorithms in digital communication, ensuring that data is transmitted accurately.
The Morse code in present days
The Morse code is pretty much a thing of the past. Although slowly, after WW2, the code was largely phased out, it remains in the hearts of amateur radio operators. There is even an International Morse Code Preservation Society, which, interestingly, has thousands of members around the globe.
There could also be a practical use for it. During emergencies, when it might be hard to make contact through other means, the Morse code might come in handy. It’s not as fast as the internet, but in case of an emergency, it’s not always about speed – initially, it’s about being able to send the message across.
As a curiosity, the US Navy is still training intelligence specialists to master the code, so while the heyday of dits and dahs may be over, Morse code still keeps pressing on.
If you want to know more about our list of services at Clever++, please visit our website.




